Table of Contents
404 Error: 7 Smart Ways to Fix Broken Pages on Your Website
1. Understanding the 404 Error
1.1 What Is a 404 Error?
A 404 error happens when someone tries to visit a page on your website, but that page doesn’t exist. Instead of showing your content, the browser displays a message like “404 Page Not Found.” This is a standard response code sent by a web server when the URL requested is invalid or missing. It’s not a virus or a hacking issue—it just means the browser can’t find the page the user asked for. These errors are very common, especially on websites that go through frequent updates or content deletions.
1.2 Why Does It Happen?
There are many reasons for a 404 page to show up. Maybe you deleted a blog post or changed its URL without adding a redirect. Sometimes, people mistype URLs. Or it could be an internal link on your site pointing to a page that no longer exists. Even external websites linking to your old pages can lead visitors to a 404 error if the link is outdated or broken.
1.3 How It Affects SEO and User Experience
If you’re thinking 404 errors don’t matter—think again. When users land on a broken page, they often leave your site right away. That means a higher bounce rate, which sends a negative signal to search engines. Also, if search engine bots crawl your website and hit too many 404s, they may reduce your page authority and indexing. In short, broken links damage SEO and hurt user trust.
2. How to Identify 404 Pages
2.1 Use Google Search Console
One of the best tools to find 404 errors is Google Search Console. It shows a list of crawl errors Googlebot has found on your site. You can see which URLs are returning 404s, when they were detected, and which pages are affected. It’s completely free and very powerful.
2.2 Try SEO Tools Like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog
Tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, and SEMrush can crawl your entire website and list all broken links. These tools also show whether those links are internal or external, helping you fix them quickly. Screaming Frog is especially useful if you’re working on a large site, as it gives you a full breakdown of status codes.
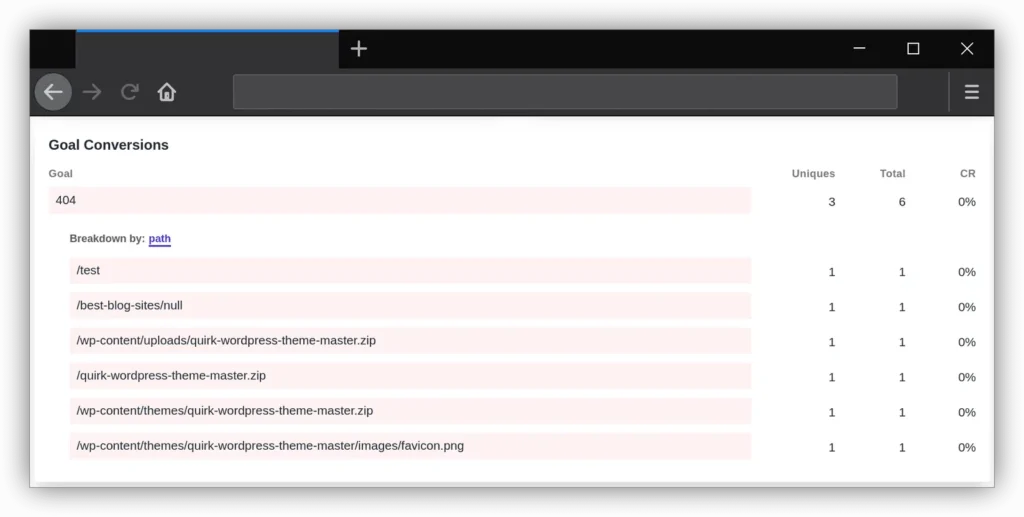
2.3 Check Site Analytics
Your website analytics can also help. Look for pages that get traffic but have a high bounce rate or low time-on-page. Sometimes, users might be landing on a broken page and leaving right away. If these pages have a high exit rate, it might be worth checking them manually for 404 issues.
3. Fixing Existing 404 Errors
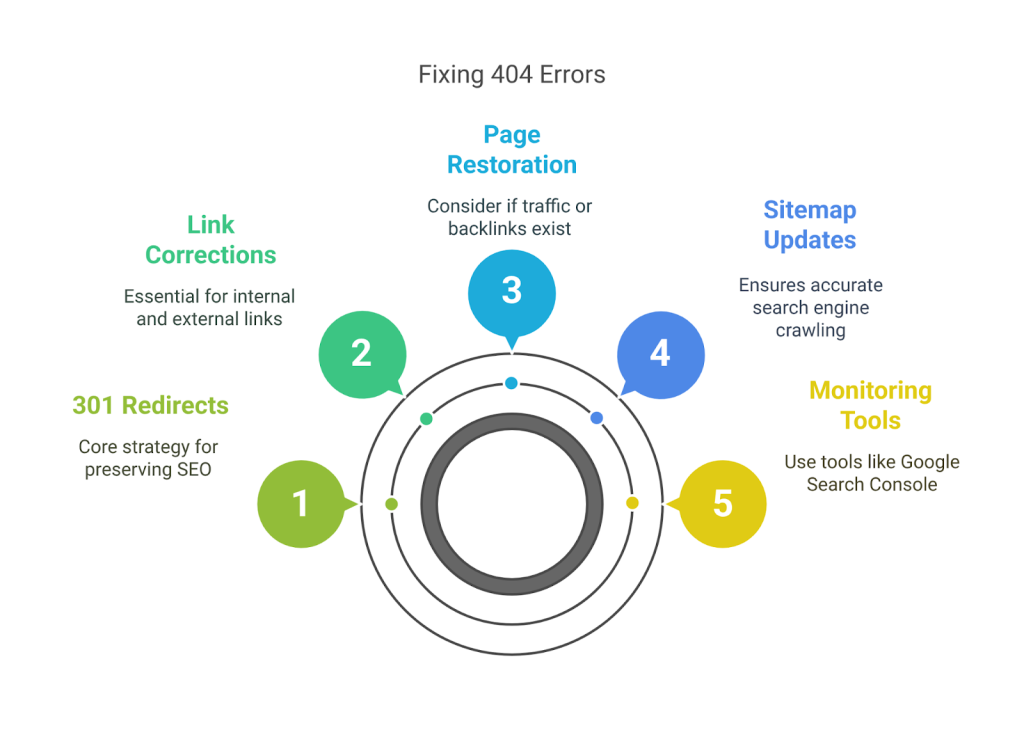
3.1 Redirect with 301
The best way to handle broken pages is to set up a 301 redirect. This tells both users and search engines that the old URL has been permanently moved to a new one. When a visitor lands on the old link, they’ll be automatically redirected to the updated page. This preserves your link equity and improves user experience.
3.2 Update Internal Links
Sometimes, broken links come from within your own site. Maybe you renamed a URL but forgot to update it on your homepage or other blog posts. Go through your internal links and correct any outdated URLs so they point to the right page.
3.3 Restore Deleted Pages (if needed)
In some cases, you might have deleted a page that was getting traffic or backlinks. If that page still has value, consider restoring it with updated content. It’s better to keep the link active than to lose traffic and authority from outside websites linking to it.
4. Preventing Future 404 Errors
4.1 Regularly Monitor Broken Links
Prevention is better than cure. Make it a habit to scan your website every month for broken links using tools or plugins. That way, you catch issues early before they become big problems.
4.2 Keep URL Structure Clean
A messy URL structure often leads to confusion and broken pages. Try to use simple and consistent URLs that don’t change unless absolutely necessary. Avoid using dates or numbers in your URL if your content is evergreen.
4.3 Don’t Delete Pages Without Planning
Before deleting any page, ask yourself: “Does this page get traffic or have backlinks?” If yes, then either redirect it or update the content instead of deleting. Only remove pages if you’re sure they bring zero value and you have a solid redirect plan.
5. Custom 404 Pages: Turn Error into Opportunity

5.1 Add Helpful Links
Your 404 page doesn’t have to be a dead end. Add links to your homepage, top blog posts, or contact page so the user can keep exploring your website.
5.2 Keep It Branded and Friendly
Make your 404 page match your brand style. Add some humor or a friendly message like “Oops! This page took a coffee break.” A fun, engaging 404 page keeps the user on your site longer.
5.3 Include a Search Bar
Add a search bar to your 404 page. This lets users quickly find what they were originally looking for, reducing bounce rate and improving navigation.
6. Testing Your Fixes

6.1 Re-Crawl with Search Console
After making changes, go back to Google Search Console and ask Google to re-crawl your site. This helps update the index and confirm your 404 errors are gone.
6.2 Manual Testing in Browser
Don’t rely only on tools—visit the fixed pages yourself. Manually check if redirects are working and if the user experience feels smooth. This is an extra but important step.
6.3 Use Browser Extensions
Extensions like Check My Links (Chrome) or Link Checker can scan any page for broken links. These are super useful when you’re reviewing content manually or auditing old blog posts.
7. Final Tips to Keep Your Site Healthy

7.1 Maintain Your Sitemap
Always keep your XML sitemap updated. Remove any deleted or broken pages and submit the latest version to Google via Search Console.
7.2 Use Broken Link Checkers
Use free or premium broken link checker tools regularly. Many plugins (like Broken Link Checker for WordPress) can alert you in real-time if any link stops working.
7.3 Keep Monitoring Every Month
Make it a monthly task to monitor your links and check crawl reports. This small habit can save you from big SEO damage caused by ignored 404 pages.
8. Conclusion
A 404 error may seem small, but if ignored, it can slowly damage your website’s SEO and frustrate your users. Thankfully, it’s also one of the easiest problems to fix if you stay on top of it. Regular checks, smart redirects, custom error pages, and link monitoring tools can help you avoid future issues. So next time you see a 404 page, don’t panic, fix it, learn from it, and improve your site for the better.
9. FAQs
1. What is a 404 error?
A 404 error means the page you’re trying to open can’t be found on the website.
2. Does a 404 error affect SEO?
Yes, too many 404 errors can harm your SEO and lower your search rankings.
3. How do I fix a 404 error?
You can fix a 404 error by setting up a 301 redirect to a working page.
4. Can I prevent 404 errors on my site?
Yes, by regularly checking for broken links and keeping your URLs clean.
5. Should I create a custom 404 error page?
Absolutely! A custom 404 error page helps users stay on your site and find what they need.
